Why is it necessary to have a root canal?
A root canal is a cavity inside a tooth that contains nerves, blood vessels, and tissue, known as pulp. Pain, inflammation, and even infection occur when the area becomes infected due to tooth decay, injury, or other causes. If a root canal is not treated promptly, it can lead to further complications, including tooth loss.
When should you contact an endodontist?
If you experience severe tooth pain, constant sensitivity to cold or heat, swollen gums around the tooth, or an abscess, it could be a sign of a root canal infection. If you have noticed these signs, you can search for “endodontist near me” for evaluation and possible treatment.
Root canal treatment process
Root canal treatment usually consists of several stages:
- Diagnosis and preparation: The endodontist takes X-rays to determine the extent of damage to the tooth and root canal. The tooth is then numbed, and the area around it is aseptically cleaned.
- Pulp removal: Using instruments, the endodontist removes infected or damaged pulp from the root canal.
- Shaping and cleaning of canals: Root canals are widened and cleaned with special instruments to remove bacteria, infected tissue, and other organic debris.
- Filling the canals: Once cleaned, they are filled with a material to prevent reinfection and preserve tooth structure.
- Tooth restoration: Typically, after root canal treatment, the tooth must be restored with a crown or other methods to restore its function and appearance.
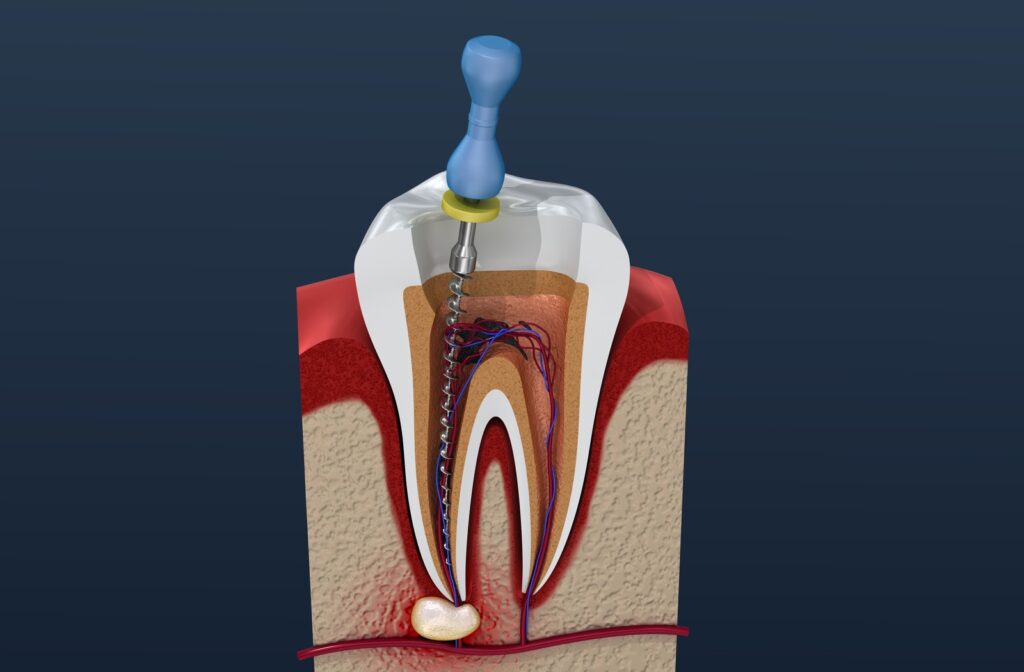
Root canal treatment, or endodontic treatment, is a procedure designed to save a tooth when the inside area of the tooth, including the nerve and blood vessels, becomes infected or damaged. This procedure can be life-saving, preventing tooth extraction and helping to maintain natural chewing function and smile aesthetics. This article will look at all aspects of root canal treatment, from understanding the process to its consequences and current trends in the field.
Pain and discomfort
Many patients fear pain and discomfort during and after root canal treatment. However, modern methods of pain relief make the procedure virtually painless. After the procedure, your doctor may recommend taking painkillers to relieve discomfort in the first days.
Benefits of root canal treatment
Root canal treatment can save the tooth, prevent infection, and keep the surrounding tissue and adjacent teeth healthy. It also helps avoid having to extract the tooth, which can lead to additional problems, including loss of chewing function and changes in the bite.
Current trends in root canal treatment:
With the constant development of the dental industry, new methods and technologies are emerging that improve the root canal treatment process. Some of these include using more precise instruments to clean root canals, using lasers to kill bacteria, and using 3-D X-rays for more accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Modern technologies have significantly improved the root canal treatment process, making it more effective and comfortable for the patient. These include:
- Microscopes allow dentists to view the root canal at high magnification, which helps remove infected tissue from even the thinnest canals.
- Use of lasers: Laser therapy can effectively kill bacteria in the root canal and promote tissue healing.
- Using variable endodontic files: These files allow for more precise cleaning and shaping of the root canal, which improves treatment results.
Care after root canal treatment
After root canal treatment, it is essential to follow your doctor’s dental care instructions and visit a dental clinic regularly to monitor the condition of your teeth and prevent possible complications.
The bottom line
Root canal treatment is necessary to save your tooth from extraction and help maintain a healthy smile. Understanding the treatment process, its necessity, steps, and consequences will help you make more informed decisions about your dental health. Feel free to discuss any questions or concerns with your dentist so you can clearly understand what to expect from the procedure.







